- Homepage
- Bestiary
- Carnivores
- Pachydermata
- Birds of prey
- Bateleur
- Buzzard, Augur
- Buzzard, Common
- Eagle, African Crowned
- Eagle, African Fish
- Eagle, Black-chested Snake
- Eagle, Brown Snake
- Eagle, Long-crested
- Eagle, Martial
- Eagle, Steppe
- Eagle, Tawny
- Eagle, Wahlberg's
- Falcon, Amur
- Falcon, Lanner
- Falcon, Pygmy
- Goshawk, African
- Goshawk, Dark Chanting
- Goshawk, Eastern Chanting
- Goshawk, Gabar
- Harrier, African Marsh
- Harrier, Eurasian Marsh
- Harrier, Montagu's
- Harrier, Pallid
- Hawk, African Harrier
- Hobby, eurasian
- Kestrel, Common
- Kestrel, Grey
- Kestrel, Greater
- Kestrel, Lesser
- Kite, Yellow-billed
- Kite, Black-winged
- Eagle-owl, Verreaux's
- Owl, african scops
- Owl, Marsh
- Secretary Bird
- Sparrowhawk
- Vulture, Egyptian
- Vulture, Hooded
- Vulture, Lappet-faced
- Vulture, Palm-nut
- Vulture, Rüppell's
- Vulture, White-backed
- Vulture, White-headed
- Ongulates
- Antelope, sable
- Bongo
- Buffalo
- Bushbuck
- Bushpig
- Dik-dik, Kirk's
- Dik-dik, Günther's
- Duiker, common
- Duiker, Harvey's
- Eland
- Gazelle, Grant
- Gazelle, Thomson
- Gerenuk
- Giraffe, masai
- Giraffe, reticulated
- Giraffe, Rotschild's
- Hartebeest
- Hog, giant forest
- Impala
- Klipspringer
- Kudu, greater
- Kudu, lesser
- Oribi
- Oryx, east african
- Oryx, fringe-eared
- Reedbuck, Bohor
- Reedbuck, mountain
- Steenbok
- Suni
- Topi
- Warthog
- Waterbuck, common
- Waterbuck, defassa
- Wildebeest
- Zebra, Grevy
- Zebra, hybrid
- Zebra, plain
- Reptiles
- Waders and water birds
- Avocet pied
- Bittern, dwarf
- Coot
- Cormorant, long-tailed
- Cormorant, white-breasted
- Courser, Bronze-winged
- Courser, somali
- Courser, Temminck's
- Courser, three-banded
- Courser, Two Banded
- Crake black
- Crane, grey crowned
- Darter, african
- Duck, african black
- Duck, knob-billed
- Duck, white-backed
- Duck, white-faced whistling
- Duck, yellow-billed
- Egret, cattle
- Egret, great
- Egret, intermediate
- Egret, little
- Flamingo, greater
- Flamingo, lesser
- Goose, egyptian
- Goose, spur-winged
- Grebe, little
- Greenshank, common
- Gull, grey-headed
- Gull, sooty
- Hamerkop
- Heron, black
- Heron, black-headed
- Heron, goliath
- Heron, grey
- Heron, purple
- Heron, rufous-bellied
- Heron, squacco
- Heron, striated
- Night-heron, black-crowned
- Ibis, african sacred
- Ibis, glossy
- Ibis, hadada
- Jacana, African
- Lapwing, Senegal
- Moorhen, common
- Painted-snipe, greater
- Pelican, great white
- Pelican, pink-backed
- Plover, blacksmith
- Plover, black-winged
- Plover, caspian
- Plover, crowned
- Plover, kittlitz's
- Plover, long-toed
- Plover, ringed
- Plover, spur-winged
- Plover, three-banded
- Plover, wattled
- Pratincole, collared
- Ruff
- Sandpiper, common
- Sandpiper, green
- Sandpiper, marsh
- Sandpiper, wood
- Sandplover, greater
- Snipe, common
- Spoonbill
- Stilt
- Stint, little
- Stork, abdim's
- Stork, african openbill
- Stork, black
- Stork, marabou
- Stork, saddle-billed
- Stork, white
- Stork, woolly-necked
- Stork, yellow-billed
- Teal, common
- Teal, Hottentot
- Teal, red-billed
- Teal cape
- Tern, white-winged
- Tern, whiskered
- Thick-knee, spotted
- Thick-knee, water
- Terrestrial birds
- Bustard, black-bellied
- Bustard, buff-crested
- Bustard, Hartlaub's
- Bustard, kori
- Bustard, white-bellied
- Francoli, coqui
- Francolin, crested
- Francolin, Hildebrandt's
- Francolin, Jackson's
- Francolin, red-winged
- Francolin, Shelley's
- Guineafowl, helmeted
- Guineafow, vulturine
- Hornbill, southern ground
- Ostrich, masai
- Ostrich, somali
- Sandgrouse, black-faced
- Sandgrouse, chesnut-bellied
- Sandgrouse, yellow-throated
- Spurfowl, red-necked
- Spurfowl, yellow-necked
- Birds
- Apalis, yellow-breasted
- Babbler, arrow-marked
- Babbler, brown
- Babbler, northern pied
- Barbet, d'Arnaud's
- Barbet, red-and-yellow
- Barbet, red-fronted
- Batis chin-spot
- Bee-eater, blue-cheeked
- Bee-eater, little
- Bee-eater, cinnamon-chested
- Bee-eater, eurasian
- Bee-eater, olive
- Bee-eater, somali
- Bee-eater, white-throated
- Bee-eater, white-fronted
- Bishop, yellow
- Bishop, Zanzibar red
- Bishop, yellow-crowned
- Boubou, tropical
- Boubou, slate-coloured
- Bulbul
- Bush-shrike, sulphur-breasted
- Bunting, cinnamon-breasted rock
- Bush-shrike, rosy-patched
- Camaroptera, grey-backed
- Canary, brimstone
- Canary, yellow-crowned
- Chat, alpine
- Chat, anteater
- Chat, cliff
- Chat, sooty
- Chatterer
- Cisticola, Aberdare
- Cisticola, desert
- Cisticola, Hunter's
- Cisticola Lyne's
- Cisticola, rattling
- Cisticola, stout
- Cisticola, winding
- Citril, african
- Cordon-bleu
- Coucal, white-browed
- Coucal, black
- Crow, house
- Crow, pied
- Cuckoo, african
- Cuckoo, african emerald
- Cuckoo, common
- Cuckoo, Diederik
- Cuckoo, great spotted
- Cuckoo, red-chested
- Dove, african mourning
- Dove, dusky turtle
- Dove, emerald-spotted wood
- Dove, namaqua
- Dove, laughing
- Dove, red-eyed
- Dove, ring-necked
- Drongo, fork-tailed
- Firefinch
- Fiscal, northern
- Fiscal, grey-backed
- Fiscal, long-tailed
- Fiscal, Taita
- Flycatcher, african dusky
- Flycatcher, african grey
- Flycatcher, african paradise
- Flycatcher, spotted
- Flycatcher, southern black
- Flycatcher, white-eyed slaty
- Go-away-bird
- Grenadier, purple
- Hoopoe
- Hoopoe, green wood
- Hornbill, african grey
- Hornbill, Jackson's
- Hornbill, Von Der Decken's
- Hornbill, red-billed
- Hornbill, eastern yellow-billed
- Hornbill, sylvery-cheeked
- Hornbill, crowned
- Indigobird, village
- Kingfisher, grey-headed
- Kingfisher, giant
- Kingfisher, malachite
- Kingfisher, pied
- Kingfisher, striped
- Kingfisher, woodland
- Lark, pink-breasted
- Lark, red-capped
- Lark, rufous-naped
- Longclaw, pangani
- Longclaw, rosy-breasted
- Longclaw, yellow-throated
- Lovebird
- Mannikin, bronze
- Mannikin, rufous-backed
- Mousebird, blue-naped
- Mousebird, speckled
- Mousebird, white-headed
- Oriole, black-headed
- Oriole, african golden
- Oxpecker, yellow-billed
- Oxpecker, red-billed
- Parrot, brown
- Parrot, red-bellied
- Pigeon, african green
- Pigeon, speckled
- Pipit, grassland
- Pipit, plain-backed
- Pipit, golden
- Quail-finch
- Quelea red-billed
- Raven, white-necked
- Raven, fan-tailed
- Robin-chat, Cape
- Robin-chat, white-browed
- Roller, eurasian
- Roller, lilac-breasted
- Roller, purple
- Rook, Cape
- Scimitarbill
- Scimitarbill, Abyssinian
- Scrub Robin, white-browed
- Seedeater, streaky
- Seedeater, yellow-rumped
- Shrike, lesser grey
- Shrike, red-backed
- Shrike, northern white-crowned
- Shrike, Isabelline
- Silverbird
- Sparrow, chesnut
- Sparrow, grey-headed
- Sparrow, rufous
- Sparrow, yellow-spotted bush
- Sparrow-Lark Fischer's
- Sparrow-weaver, Donaldson-Smith's
- Sparrow weaver, white-browded
- Starling, black-bellied
- Starling, bristle-crowned
- Starling, Fischer's
- Starling, Golden-breasted
- Starling, greater blue-eared
- Starling Hildebrandt's
- Starling, red-winged
- Starling, Rüppell's
- Starling, slender-billed
- Starling, superb
- Starling, violet-backed
- Starling, wattled
- Sunbird, amethyst
- Sunbird, beautiful
- Sunbird, bronze
- Sunbird, eastern double-collared
- Sunbird, golden-winged
- Sunbird, Hunter's
- Sunbird, malachite
- Sunbird, mariqua
- Sunbird, eastern violet-backed
- Sunbird, purple-banded
- Sunbird, scarlet-chested
- Sunbird, scarlet-tufted malachite
- Sunbird, tacazze
- Sunbird, variable
- Swallow, barn
- Swallow, red-rumped
- Swallow, lesser striped
- Swallow, wire-tailed
- Tchagra, black-crowned
- Tchagra, brown-crowned
- Thrush, abyssinian
- Thrush, common rock
- Thrush, spotted morning
- Tit, red-throated
- Tit, white-bellied
- Wagtail, african pied
- Wagtail, western yellow
- Warbler, grey-capped
- Warbler, moustached grass
- Warbler, willow
- Waxbill, common
- Weaver, african golden
- Weaver, Baglafecht
- Weaver, black-capped social
- Weaver, chesnut
- Weaver, grey-capped social
- Weaver, grosbeak
- Weaver, Holub's golden
- Weaver, northern masked
- Weaver, parasitic
- Weaver, red-billed
- Weaver, red-headed
- Weaver, spectacled
- Weaver, speckle-fronted
- Weaver, Speke's
- Weaver, Taveta golden
- Weaver, village
- Weaver, vitelline masked
- Weaver, white-headed buffalo
- Wheatear, abyssinian black
- Wheatear, capped
- Wheatear, isabelline
- Wheatear, northern
- Whinchat
- Whydah, paradise
- Whydah, pin-tailed
- Widowbird, Jackson's
- Widowbird, red-cowled
- Widowbird, white-winged
- Widowbird, yellow-mantled
- Woodpecker, grey
- Wodpecker, nubian
- Wren-Warbler , Grey
- Primates, Rodents and Others
- Baboon, olive
- Baboon, yellow
- Colobus, angolan
- Colobus, guereza
- Galago, greater
- Hare
- Hyrax, rock
- Hyrax, bush
- Mongoose, banded
- Mongoose, dwarf
- Mongoose, slender
- Mongoose, white-tailed
- Mole rat, naked
- Monkey, blue
- Monkey, patas
- Monkey, vervet
- Porcupine
- Rat, afroalpine vlei
- Squirrel, unstripped ground
- Squirrel, ochre bush
- Squirrel, red bush
- Chiromantis petersii
- B&W Gallery
- Buy prints
- Contact
Carnivores Pachydermata Ongulates Reptiles Primates, rodents and others Birds Birds of prey Terrestrial birds Waders and water birds
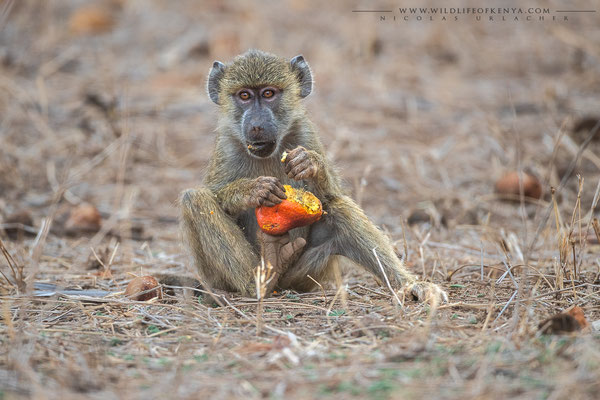
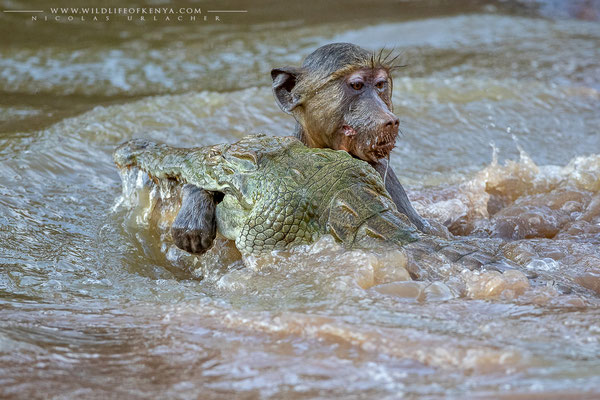
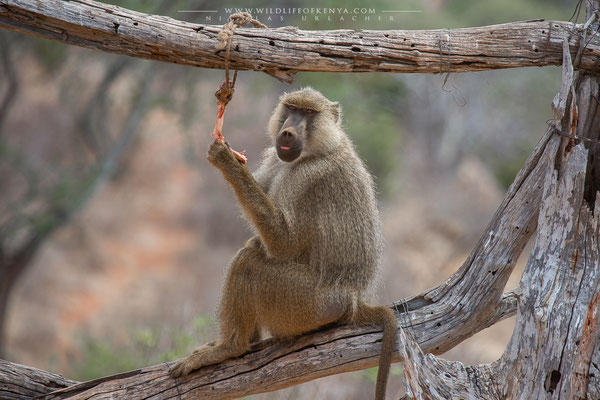
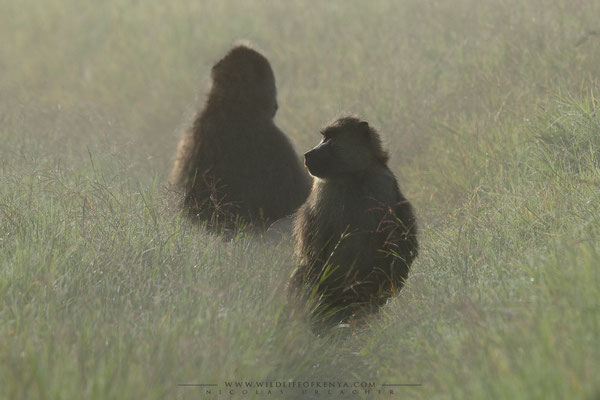
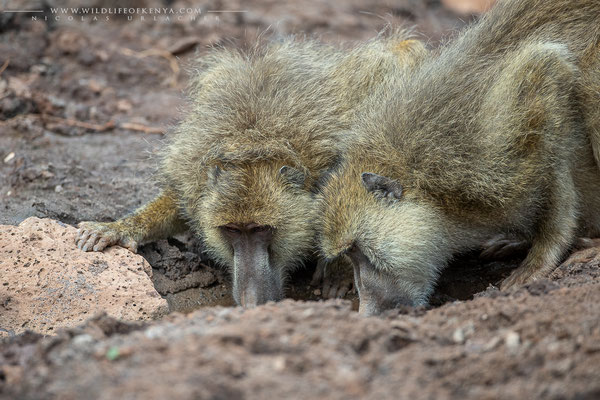
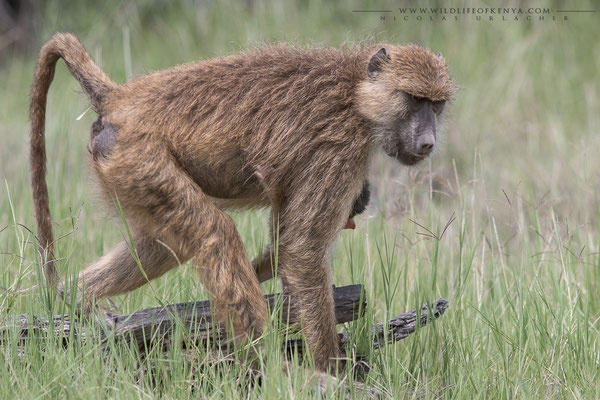
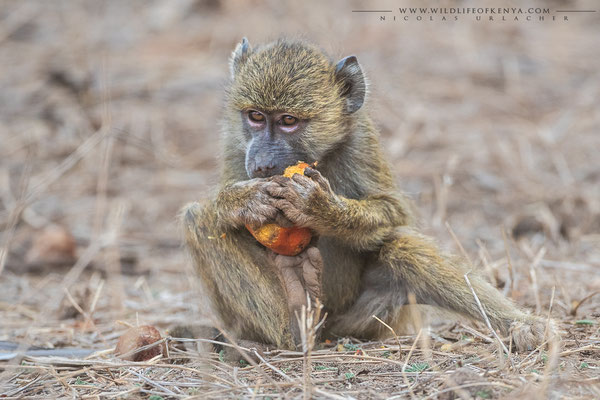
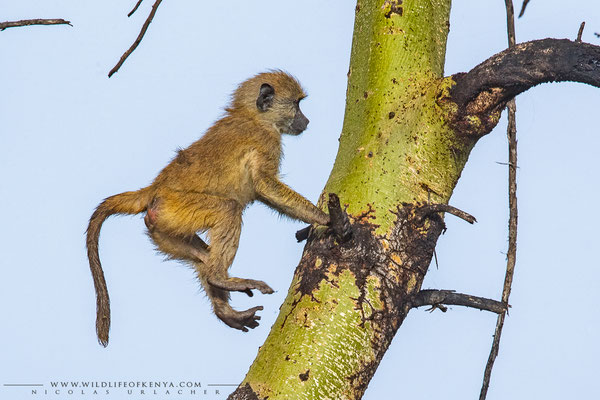
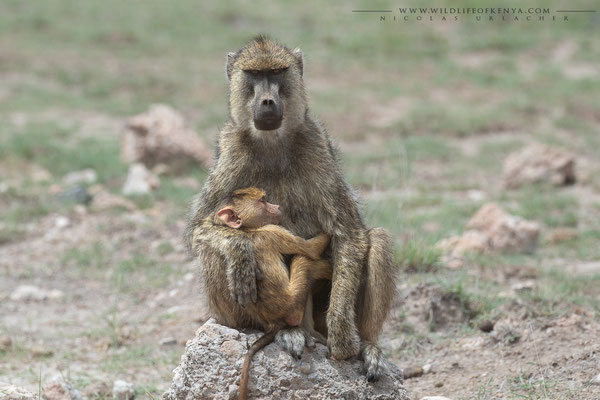
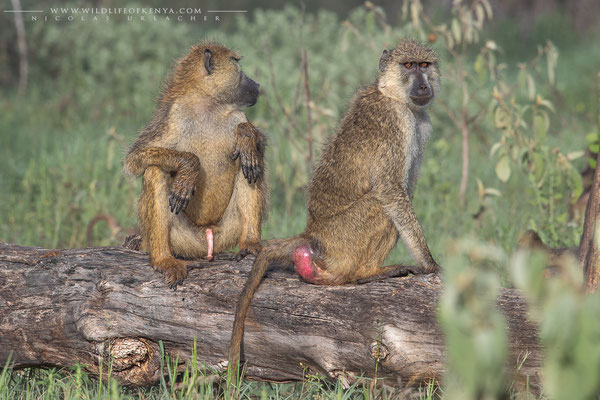
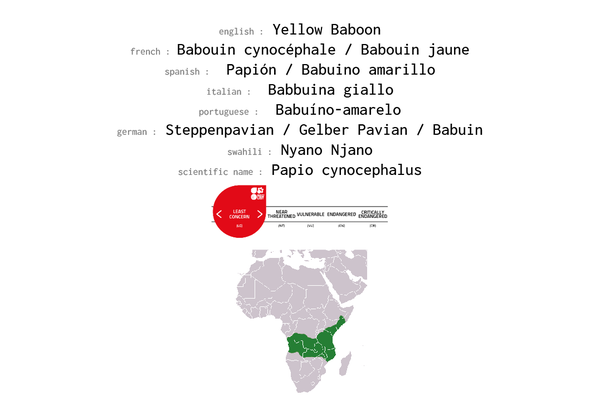
Yellow Baboon
The yellow baboon (Papio cynocephalus) is a baboon in the family of Old World monkeys. The species epithet literally means "dog-head" in Greek, due to the dog-like shape of the muzzle and head. Yellow baboons have slim bodies with long arms and legs, and yellowish-brown hair. Yellow baboons inhabit savannas and light forests in eastern Africa, from Kenya and Tanzania to Zimbabwe and Botswana. They are diurnal, terrestrial, and live in complex, mixed-gender social groups of eight to 200 individuals per troop. They are omnivorous with a preference for fruits, but also eat other plants, seeds, grasses, bulbs, leaves, bark, blossoms and fungi as well as worms, insects, birds, rodents and small mammals. All baboons are highly opportunistic feeders and will eat virtually any food they can find.
Yellow baboons use at least 10 different vocalizations to communicate. When traveling as a group, males will lead, females and young stay safely in the middle, and less-dominant males bring up the rear. A baboon group's hierarchy is such a serious matter, and some subspecies have developed interesting behaviors intended to avoid confrontation and retaliation. For example, males have frequently been documented using infants as a kind of "passport" or shield for safe approach toward another male. One male will pick up the infant and hold it up as it nears the other male. This action often calms the other male and allows the first male to approach safely.
Baboons are important in their natural environment, not only serving as food for larger predators, but also by dispersing seeds in their waste, and their messy foraging habits. They are also efficient predators of smaller animals and their young, keeping some animals' populations in check.
Source : Wikipedia